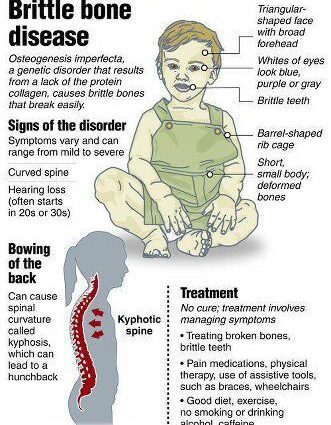
What are the symptoms of Osteogenesis Imperfecta?
преломи observed during osteogenesis imperfecta occur on long bones (especially those of the lower limbs) and flat bones (ribs, vertebrae). Fractures of the femur are the most frequently observed. These fractures are often horizontal, slightly displaced and consolidate within the same timeframe as fractures occurring in normal bone. The occurrence of these fractures decreases with age especially in women from puberty to menopause thanks to the production of estrogen.
деформације костију (femur, tibia, ribs, pelvic bone) occur spontaneously or are related to vicious calluses. Spinal compression can be the cause of frequent deformities of the spine (scoliosis).
An upward displacement of the occipital foramen (opening at the level of the base of the skull allowing the spinal cord to pass through) characterizes cranial deformations (also called “basilar impression”). Headaches (headaches), sharp osteotendinous reflexes with weakness of the lower limbs or damage to the cranial nerves (trigeminal nerve) are complications of these cranial deformities and justify the practice of nuclear magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). ). Finally, the face can be a little deformed (triangular appearance with a small chin). X-rays of the skull make it possible to highlight Wormian bones (resembling supernumerary bones and linked to a defect in ossification).
Short stature is frequently seen in osteogenesis imperfecta.
Finally, other manifestations are possible:
- заeye damage (sclera) with a bluish appearance of the white of the eye.
– Ligament hyperlaxity, present in more than two thirds of patients, can be responsible for flat feet.
– deafness which can occur in childhood is common in adulthood. It is never deep. Hearing loss is linked to damage to the inner or middle ear. These abnormalities are linked to poor ossification, the persistence of cartilage in normally ossified areas and abnormal calcium deposits.
– nosebleeds and bruises (especially in children) testify to the fragility of the skin and capillaries.
– dental damage called дентиногенеза имперфекта. It affects both milk teeth (which are smaller than normal) and permanent teeth (bell-shaped appearance, narrowed at their base) and corresponds to a fragility of the dentin. The enamel splits easily leaving the dentin exposed. These teeth wear out very prematurely and abscesses can develop. It gives the teeth an amber color and makes them more globular. Certain families present genetically transmitted dental defects, quite identical, without evidence of osteogenesis imperfecta.
– finally, cardiovascular abnormalities have been reported in adults: aortic regurgitation, mitral valve prolapse, mitral insufficiency, dilations, aneurysms or rupture of the cardiac cavities, the aorta or cerebral blood vessels.
Variable severity
The disease varies in severity from patient to patient and all of the symptoms described are rarely present in the same patient. Due to this great clinical variability (heterogeneity), a classification of the forms of the disease (Sillence classification) is used and includes four types:
- Le type I : the most frequent moderate forms (few fractures and deformations). Fractures are usually seen after birth. The size is close to normal. The sclera are blue in color. Dentinogenesis imperfecta is observed in type IA but absent in I B. Skull x-rays reveal a speckled appearance (islands of irregular ossification)
- the type II : serious forms, incompatible with life (lethal) due to respiratory failure. X-rays show long crumpled bones (accordion femur) and rosary ribs
- type III : severe but not fatal forms. Fractures are observed early and quite often before birth; Symptoms include a deformity of the spine (kyphoscoliosis) and short stature. The sclera are variable in color. There may be imperfect dentinogenesis.
- type IV : of intermediate severity between type I and type III, it is characterized by white sclera, deformations of long bones, skull and vertebrae (flattened vertebrae: platyspondyly). Dentinogenesis imperfect is inconstant.